Glasshouses are simple house structure's but all surfaces are glass so that light can penetrate through to the interior.

How glasshouses work:
1. Solar radiation - initial source of energy in the form of light.
2. Light is able to penetrate through the glass to the internal surfaces
3. Light is absorbed by surfaces inside the glass house e.g. the soil, the plants.
4. The surfaces will re emit the energy as heat.
5. the heat, warms the air and rises it's average kinetic energy and the temperature increases.
6. The warm air is trapped, it cools at the upper surfaces and sink to the floor to be rewarmed.
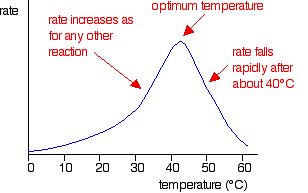
How does this affect crop yield?
warm air in glasshouse -----------> increase in crop yield
1. This has to do with the relation between temperature and the rate of reaction.
The higher temperatures in the glass house are closer to the optimum temperature for enzyme reactions inclusing Photosynthesis.
2. Also, it provides constant temperatures and so constant productions.
3. Prevention of loss of water vapor
4. Avoids frost damage, particularly to seedlings.
5. Glasshouses are often warmed by the burning of fossil fuels:
a) increase in the carbon dioxide levels in glasshouse. Increase concentration of the substrate for photosynthesis which mean more product and growth.
b) Ethene ------> stimulates fruit ripening.
No comments:
Post a Comment