Remember that mitosis is a form of cell division which results in growth. And that growth occurs by an increase in the number of cells.
The number of chromosomes in the nucleus is called the diploid number (2n)
For humans 2n = 46, for cats 2n = 38.
In the process of mitosis, the cell will divide into two cells both with a nucleus each. Inside the nucleus we find that each cell has a diploid nucleus. These cells are identical. Sometimes called daughter cell.
They have the same number of chromosomes and they have the same set of chromosomes.

3.24 b. Understand that the division of a diploid cell by mitosis produces cells which contain identical sets of chromosomes.
The initial cell has to copy the chromosomes it has. Copying the chromosomes is a process called DNA replication. In this process each chromosome undergoes a copying process to form an identical copy of itself.
With all the same gene and alleles and these two copies are held together by a structue arround the center region known as the centro-mere (Holding the two chromosomes together).
We refer to these cells as a pair of Chromatids.
during this process the nucleus is still intact. Which means you cannot see this process happening.
This is known as the Interphase of the cell cycle.
3.24 c.
DNA replication occurs during the Interphase
First sing that a cell is entering the process of mitosis, is when we see the break down of the nuclear membrane. The nucleus breaks down.
This is a phase known as the pro phase. When it breaks down, the chromosomes become visible.
With the nucleus gone, inside the cell a network of protein molecules known as the spindle, and the spindle fibers, and these extend from one pole of the cell to the other.
What occurs during late prophase, is that the chromosome pair will move toward the spindle and join one of them at the Centromere.
Next we have the Metaphase. During which the chromosomes are in the middle arranged along the equator of the cell.
Then we have the Anaphase. In the Anaphase the fiber shortens pulling the two Chromatids appart.
Here we have the separation of the pair.
The end of mitosis is at the stage of Tilophase. When the nucleus begins to reform around the chromosomes at either end of the cell. this will be the new nucleus of the new cell.
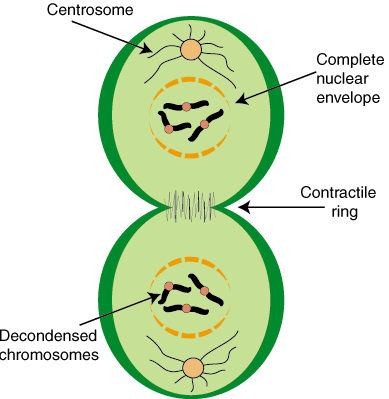
A phase know as cytokinesis where the cell splits into two (this isn't regarded as part of mitosis)